It is not a secret that chefs have experienced a steep rise to celebrity status with their ability to reach millions of people through multimedia channels. By creating new dishes and combining new flavors, these chefs offer their craft as art, each infused with their own personality, to deliver unique eating experiences that adapt and evolve with ever-changing trends and tastes.
Instructional designers have experienced the rise of the Internet, mobile devices and an ever increasing array of software tools and platforms giving them the ability to reach more learners in different ways than ever before. There appears to be a parallel between the creative work of the chef and the creative work of the instructional designer when developing either elearning, virtual classroom, instructor-led training or any blended training and development program.
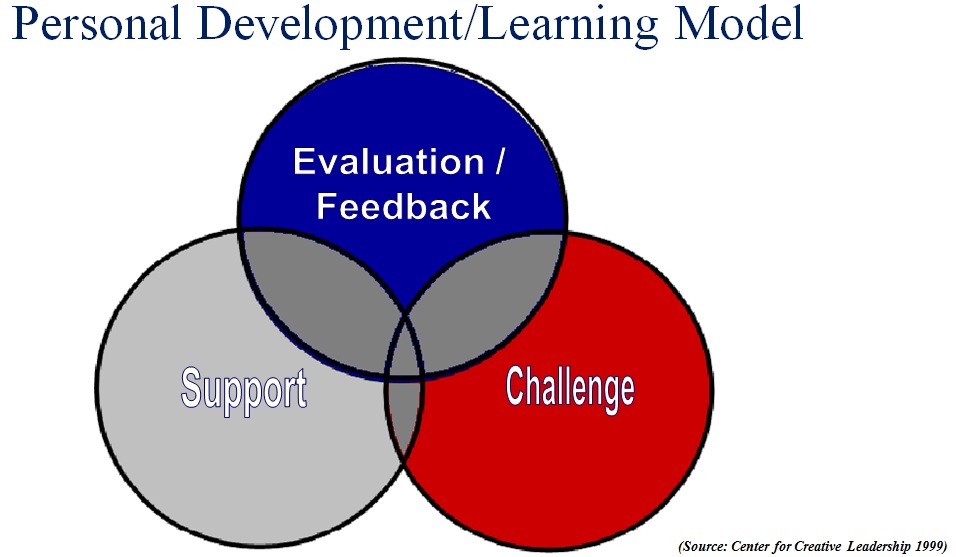
Let’s start with success. The success of the chef is delivering a great (delicious) eating experience. The success of the instructional designer is delivering an effective learning experience. Defining an effective learning experience can merit an article on its own but let’s extrapolate a definition from the model of personal development of the Center for Creative Leadership which states that you must strike the right balance between: challenging, supporting, and evaluating individuals. This would mean that instructional designers must deliver recipes that strike the right balance between these three factors.
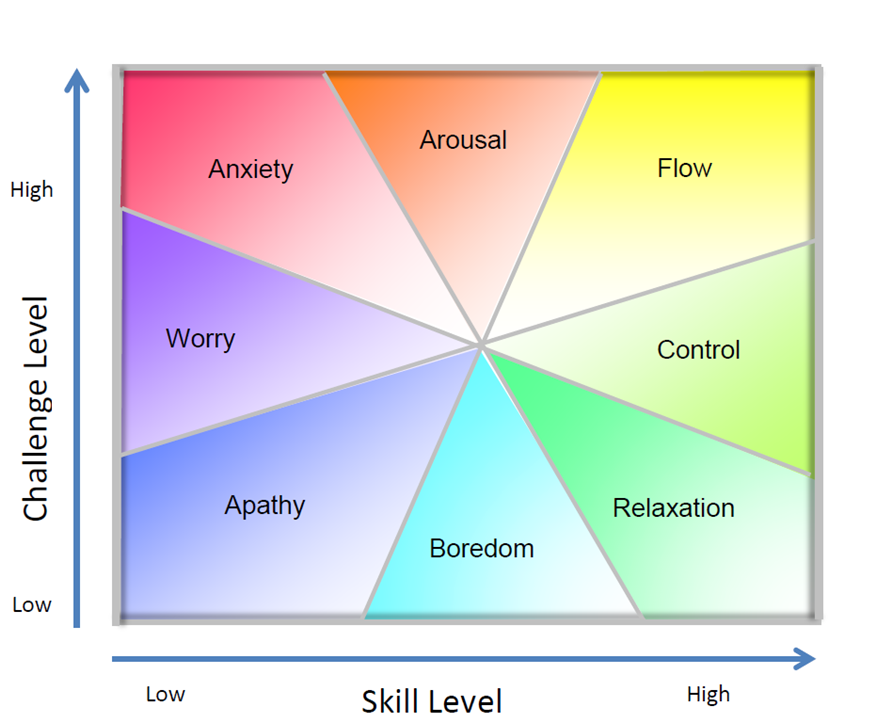
The chef uses the best ingredients and brings them together to create palate bliss. For the instructional designer, the ingredients are the principles of adult learning and the subject matter. The instructional designer has to use the principles of adult learning and the subject matter expertise to deliver a learning experience that will strike the right balance between challenging, supporting and evaluating the learner. When this balance is achieved, the instructional designer can generate the state of flow in the learners. Otherwise, individuals will be either bored if not challenged, worried if not supported, or lost if not evaluated. As an illustration, here is a graph from Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi that depicts the emotional state of the learner depending on the level of challenge versus skill level.
Every time an instructional designer delivers a learning experience that generates flow within the learners, they have created learning bliss, much like the celebrity chef creates palate bliss when the delicacies are consumed. So to all the instructional designers who every day strive to become celebrities: bon appétit!