Blog
Welcome to our Blog!
Take a look at our custom eLearning thoughts in action. We hope you find insights that will be relevant and helpful.
ArchivesWhy Pay Attention to Games?
Games are masters at engaging us. The success of “The Legend of Zelda,” “World of Warcraft,” “Second Life” and “Candy Crush” bears witness to this.
Because of that success, gamification — the strategy of bringing elements of a game to real-world experiences — has become a buzzword in the learning world.
There is evidence that games, composed of goals, rules and interactions that involve mental or physical stimulation, have been around since 2600 B.C. They are present in virtually all cultures, precisely for their ability to engage. They engage us to learn, act, fail and repeat this process toward the achievement of a self-accepted goal, out of our own free will or volition. According to Jane McGonigal, author of “Reality Is Broken: Why Games Make Us Better and How They Can Change the World,” this free will is manifested in the more than 3 billion hours a week people spend gaming globally.
Researchers say the main reason we engage in games is because of their ability to appeal to our intrinsic desires or motivators. Motivational factors can have a direct effect on learning transfer. Motivation involves self-efficacy, a cognitive force concerned with what an individual can do rather than what skills he or she may actually possess. In other words, self-efficacy is the judgment an individual makes about his or her abilities to perform a given task. In games, self-efficacy manifests when people continuously re-engage, even after failing repeatedly, because they believe they will succeed in the next round, life or level.
Game designers use strategies to leverage intrinsic motivators to attain long-term engagement. McGonigal classifies these motivators into four categories: achieving satisfying work, experiencing success or the opportunity of success, making social connections and having purpose or meaning.
Satisfying work is defined as work that produces desirable and visible results. The opportunity and hope of achieving success is a powerful stimulus that feeds our desire to improve. Social connections allow us to be recognized and appreciated, both powerful motivators. Having purpose or meaning is perhaps the most powerful motivator since, when something bigger than ourselves drives us, we are better able to overcome obstacles.
There is no doubt that awareness is growing about the benefits of appealing to intrinsic motivators to engage individuals in learning programs and ensure successful learning transfer. Our challenge in the corporate learning and development arena is to seize opportunities in which we can find creative, innovative and cost-effective ways to leverage intrinsic motivators.
To help learning and development practitioners in this endeavor, the first step is to continue to study how game designers creatively make participants learn, act, fail and repeat this process out of their own free will until they reach a predetermined goal.
Featured in Blog January 2, 2018A happy and successful 2018!
Thank you for trusting us with your learning needs and for inviting us to collaborate and contribute to your success.
Wishing our Facilitador friends and family a healthy, happy, inspiring and amazing 2018!
Featured in Blog August 7, 2017“Do or do not, there is no try” – Learn, Apply, Know?
 -Student : Master Yoda, I have some questions about “Do or do not, there is no try.”
-Student : Master Yoda, I have some questions about “Do or do not, there is no try.”
–Master Yoda : Yes.
–Student : Can I learn something and not apply it? Can I learn something and not be ready to apply it? If I learned something doesn’t that mean that I can use it? If I can use it, then why don’t I? If I know it, then why not apply it? If I don’t apply it, do I know it? If I apply it, I know it? If I apply it, I get to know it? If I learned it, then why do I know it, only after I apply it?
–Master Yoda : To learn is potential. To apply is actual. To know is experience.
–Peter Drucker: There is no substitute for experience.
(Disclaimer : the conversation is entirely my creation and it did not happen in the movie, just in case there were any doubts)
Featured in Blog September 6, 20167 Tips to Keep Your eLearning Project on Track
Nothing guarantees an eLearning project’s success or failure more than your stakeholders not understanding clearly what is expected of them. Here are some tips on how to do an amazing job setting and explaining the right expectations to keep your project on track:
1) Set up a project kick-off call or meeting: In this meeting, explain the entire process and clearly define tasks, responsible parties and timelines.
2) Create a project plan that lays all this out. Make sure to have all stakeholders review and approve. Create accountability!
3) Make sure to agree on stylesheets and brand guidelines for the project.
4) When feedback on design documents, storyboards, graphical user interfaces, graphical elements, built courses, etc. is needed, make sure you clearly explain what they are reviewing, what kind of feedback you are expecting of them, how you want them to provide it, and by when.
5) If there are multiple stakeholders providing feedback, make sure they compile the feedback in one place and agree on it. Many times when this step is skipped, contradictory feedback might make the process longer with back and forth questions and needed explanations.
6) Version control is important! Make sure you have a good and intuitive internal system in place to ensure no version control issues arise mid-project.
7) Good and constant communication between all stakeholders will ensure expectations are explained, red flags or delays are discussed and progress is tracked and celebrated.
Follow these steps and you will never again here the much dreaded words: “You never told me that!”
Featured in Blog July 27, 2016Are You Preparing Your New Hires to Succeed or Fail?
Does the training for new hires match the job?
– “No.”
– “Yes.”
– “Maybe.”
– “We are not sure.”
These are some of the answers we constantly hear. When these answers are provided, then common follow-up questions sound like this:
– “What is the training for?”
– “Isn’t it to improve performance on the job?”
– “Yes, but it is about developing the individual.”
– “But isn’t the purpose of developing the individual so that s/he can improve his/her results and hence the results of the organization?”
– “Yes and yes. OK great so does the training for new hires match the job so they know what to do when they start?”
Sadly, the answer at the end of the day is “No” in many organizations.
It is important to instill a sense of excitement to welcome new hires and provide them with the tools to be successful. Background knowledge of the company and how it started is always good but it won’t improve their abilities to succeed. Many of the content topics covered in new hire training are not centered around the question of what will help the new hires succeed. Research has pointed to the fact that nothing will improve their ability to succeed more than they themselves believing they can succeed. If this is the case, then building the confidence of new hires should be goal number one.
What is the best way to achieve this? By modeling the new hire training around the actual job they will do. This will not only provide context and meaning to the instruction but it will build the confidence of the new hire by showing them that they can do the job.
A way to start is to break down the job into its most important tasks and then work your way back from there by making those steps the topic outline of your new hire training. If you provide all the background knowledge within the context of how it impacts and fits within their job, then you will succeed in eliminating unknowns and boosting your new hires confidence to succeed. Ultimately, this is the best guarantee for a successful new hire training initiative.
Featured in Blog June 29, 2016Are you Encouraging or Discouraging Your Learners?
I may learn something new but it doesn’t necessarily mean that I am ready to apply it. Many times I learned great concepts that made sense and was eager to use or implement. However, when I tried using them for the first time, reality hit. I was bombarded with all the variables that reality brings and it was not easy to actually apply what I had just learned.
When this happens, research tells us that this discourages individuals from attempting to apply what they learned again. As adult learners we are sensitive about making a fool out of ourselves and especially in front of others. The result is that the concept I was thrilled to implement goes to waste.
What do we do as instructional designers if we don’t have the budgets or the time to build full-fledged simulations that try to recreate reality?
I want to suggest that the key is to consider the following question:
How will the learners use the knowledge when they are back on the job?
Given the answer, you can then devise strategies for providing scaffolds that support the acquisition of competence in the application of the new knowledge. Think of training wheels for a bicycle so that the learner can feel confident they won’t fall or make a fool of themselves in attempting to apply the new knowledge. This way, you can prevent your learners from becoming discouraged to apply what they’ve learned.
Featured in Blog May 31, 2016Can a Question Demonstrate the Value of Learning?
If we start from the premise that any training or learning and development investment is an investment in the individuals that participate in that training event, then it follows that those individuals are the ones who are best suited to determine the worth and merit of that training event. Isn’t this obvious and don’t most organizations allow for that? The answer is sadly no.
Surveying the participants is definitely the right move but not before, during or immediately after the training event. It is about allowing a span of time to pass so integration or learning transfer occurs. It is only when the participants are back on their jobs facing the realities of unexpected challenges and ever-changing conditions that they can determine how the training investment better equipped them to succeed. This determination may change with time and this is why it makes sense to measure it more than once at different intervals.
Therefore, what is the question we need to ask at different intervals after the training event? The answers to this two-part question, when documented and systematically organized, can demonstrate the link between learning investments and positive business results. We’d like to suggest it is: Since you participated in XYZ training event, how have you improved yourself and what results have you achieved due to those improvements?
It really can be that simple.
To learn more about this approach, take a look at our new article in CLO Magazine on the value of documentation: http://bit.ly/1OtIqRd
Featured in Blog April 7, 2016Don’t Lose Focus: Optimizing Technical Training for the Business
 Optimizing technical training for the business is a challenge that learning and development departments must meet in order to advance the goals of the organization. Usually a lot of technical information is available and it is not easy to discern and identify what needs to be taught to each of the different employee groups or stakeholders such as front-line leaders, marketing and sales departments or distributors.
Optimizing technical training for the business is a challenge that learning and development departments must meet in order to advance the goals of the organization. Usually a lot of technical information is available and it is not easy to discern and identify what needs to be taught to each of the different employee groups or stakeholders such as front-line leaders, marketing and sales departments or distributors.
Usually technical teams will have the best intentions and these are manifested in their desire to be thorough and cover everything possible about the given technical process, product or service. These good intentions lead to the creation of training programs that contain a lot of data and information. Essentially, I have seen these training programs become what I refer to as an information dump – and sometimes they can be pretty stinky!
Life can be easier for the technical team and for the training team if they consider the first question of our guiding principles when designing training programs. This question is: How will the learners use the knowledge when they are back in their job? Answering this question from the perspective of each different group of employees and stakeholders allows instructional designers to start identifying what will be most useful. In addition, by considering these different perspectives we can create guidelines for the subject matter experts (SMEs) to discern what of their expertise will be most useful. For example, if the stakeholders are managers, SMEs would put more emphasis on the technical knowledge needed to manage the technology and less towards understanding all the details of the technology.
As obvious as this sounds, it is important to focus on what is important for the “other”. It is not about the “I” (what I think is important as a technical expert), rather it is about what information is a “need-to-know” for the learner to achieve peak performance at their specific position within the organization.
Featured in Blog March 2, 2016What Could Be the #1 Enemy of Good Instructional Design?
All of us have heard the statistics about the amount of actual knowledge that gets implemented back on the job from a training program. Most researchers have estimated that only ten percent or less actually transfers. So for every $100 we are investing in a training program we are only putting to work ten dollars- and according to other researchers it could be a dismal five dollars or less. When you factor in the fact that of those $100 invested a big portion may have been spent in travel and/or logistics, then this estimation of five dollars or less is actually quite generous.
Here is the tough part, that has cost me years to understand, the responsibility of transfer is, most often than not, seen as belonging to the instructional designer or training and development department. Many others within the organization wash their hands and expect the instructional designer to wave a magic wand delivering individuals who are ready to apply what they have learned. And here in lies the culprit, the number one enemy of the absolute best instructional design is lack of opportunity to apply what I have learned. It sounds deceptively simple but not letting me put into action what I have learned doesn’t allow me to truly transfer to the physical world what I have learned.
The simple application of knowledge to a novel task is called ‘reproductive transfer’ and when there is adaptation, mutation and enhancement it is referred to as ‘productive transfer’ (Robertson, 2001) which is what we want to happen. But again, I have to be given the opportunity to apply what I have just learned. If the organization does not take this into account, the best instructional design will fail. Keep it simple by all of us agreeing – operations, marketing, sales and training – how individuals will apply what they learn before we start designing.
Featured in Blog January 28, 2016Celebrity Chefs versus Celebrity Instructional Designers?
It is not a secret that chefs have experienced a steep rise to celebrity status with their ability to reach millions of people through multimedia channels. By creating new dishes and combining new flavors, these chefs offer their craft as art, each infused with their own personality, to deliver unique eating experiences that adapt and evolve with ever-changing trends and tastes.
Instructional designers have experienced the rise of the Internet, mobile devices and an ever increasing array of software tools and platforms giving them the ability to reach more learners in different ways than ever before. There appears to be a parallel between the creative work of the chef and the creative work of the instructional designer when developing either elearning, virtual classroom, instructor-led training or any blended training and development program.
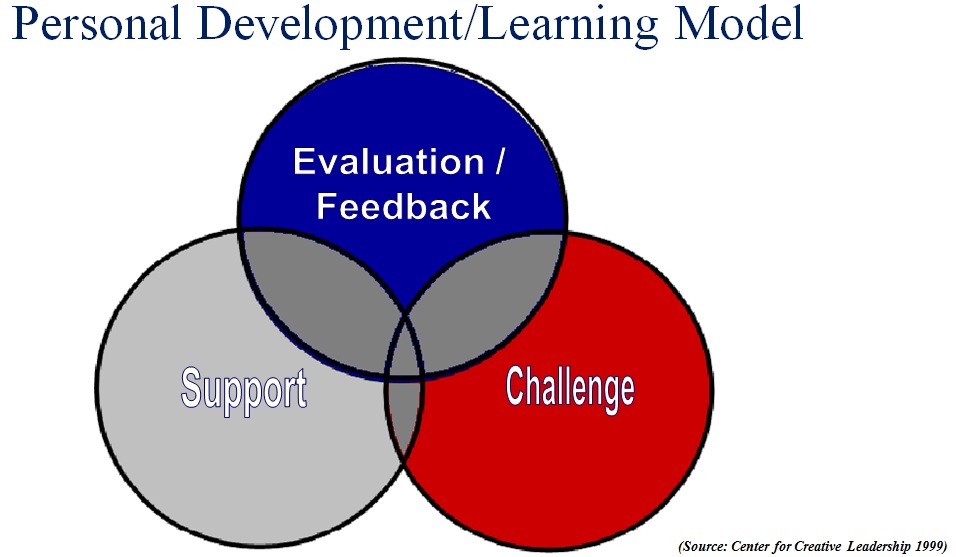
Let’s start with success. The success of the chef is delivering a great (delicious) eating experience. The success of the instructional designer is delivering an effective learning experience. Defining an effective learning experience can merit an article on its own but let’s extrapolate a definition from the model of personal development of the Center for Creative Leadership which states that you must strike the right balance between: challenging, supporting, and evaluating individuals. This would mean that instructional designers must deliver recipes that strike the right balance between these three factors.
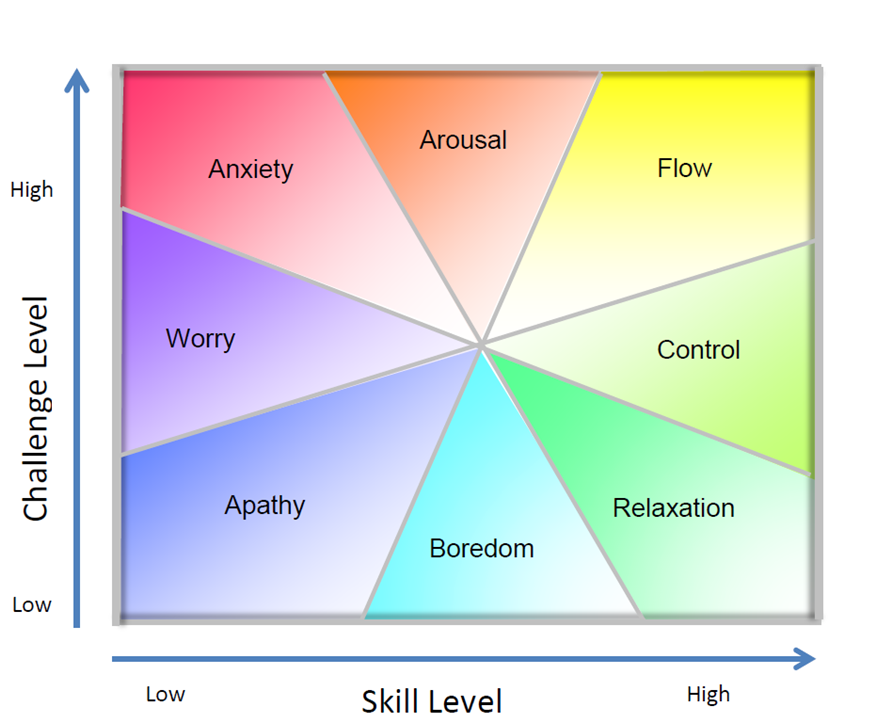
The chef uses the best ingredients and brings them together to create palate bliss. For the instructional designer, the ingredients are the principles of adult learning and the subject matter. The instructional designer has to use the principles of adult learning and the subject matter expertise to deliver a learning experience that will strike the right balance between challenging, supporting and evaluating the learner. When this balance is achieved, the instructional designer can generate the state of flow in the learners. Otherwise, individuals will be either bored if not challenged, worried if not supported, or lost if not evaluated. As an illustration, here is a graph from Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi that depicts the emotional state of the learner depending on the level of challenge versus skill level.
Every time an instructional designer delivers a learning experience that generates flow within the learners, they have created learning bliss, much like the celebrity chef creates palate bliss when the delicacies are consumed. So to all the instructional designers who every day strive to become celebrities: bon appétit!
Featured in Blog December 30, 2015Here’s to a healthy, successful and inspiring 2016
As the year comes to an end, we are grateful for the projects we have been able to contribute to. Through these projects we know we are impacting the lives of many for the good. When our clients invest in developing their talent and partner with us to create success opportunities for their employees, they allow us to fulfill our mission to expand knowledge and bring about progress. With this in mind, we want to suggest the following questions that can help training and development departments fortify their position within organizations as value creators instead of cost centers:
– Can we implement strategies to further demonstrate the value we bring to the organization, through success stories and tangible business results that can linked back to the training investments?
– Can we demonstrate how the acquisition of experience is accelerated through the programs we create?
– Can we anticipate the training needs of our internal clients?
– Can we look into strategies to replicate our top performing employees and support them on the job?
– Can we inject fun, excitement and a little intrigue into our programs to enhance perceived value and generate more participation?
We are excited to explore these questions with you in 2016!
Wishing you and yours a healthy, happy, prosperous and inspiring new year.
Featured in Blog November 24, 2015When you Ass-u-me: Adult Learning and Motivation
Can you train an adult who is not motivated to be trained? Can you motivate an adult to learn? Anybody who has trained adults will tell you that when motivation is present learning occurs, one way or another, because the individual will be able to overcome frustration, disappointment or any other obstacle that gets in the way. The opposite is also true: when motivation is not present it is practically impossible to train someone.
So if motivation is essential, why do we forget as instructional designers to incorporate methods to motivate individuals to make the best of the training and development programs we create? In my opinion the culprit is assuming our learners are motivated to learn. As Felix Unger in an episode of The Odd Couple says: “When you ass-u-me you make an ‘ass of u and me’!”
The Research
The fact that motivation is important for adults is not new. E.C. Lindeman’s in The Meaning of Adult Education in 1926 noted that adults are motivated to learn as they experience needs. The late renowned psychologist, Carl R. Rogers, stated that adults will learn only those things they perceive will help them enhance themselves, clearly underlining the value of relevancy for the adult learner. Recent research has summed it up to two basic questions adults will ask themselves before they engage in learning:
- Is it worth it?
- Can I do it?
The first question hits on the concept of motivation, since the adult learner is asking if what they are about to learn is worth their time and effort.
How to Avoid It
As good instructional designers we have to start by understanding our audience and their motivation and can’t simply assume individuals are motivated to learn because the training program is mandatory, necessary for advancement, or a high-potential leadership development program, for example. We need to incorporate strategies that address the needs for adult learners to align their own needs, aspirations and desires with the objectives of the elearning, virtual classroom, instructor-led, game, simulation or blended training program we are designing. It starts with basic questions such as:
— Have we done a good job in sharing how individuals will benefit? (This question addresses the external or extrinsic motivators that may be leveraged).
— Have we shared how others have benefited and what they have been able to accomplish? (This question is intended to ensure the creation of a vicarious experience that leads the learner to determine that it can be done).
— Have we leveraged communication, recognition, or other strategies to stimulate positive behavior before, during and after the training? (This question addresses the internal or intrinsic motivators).
In summary, have we respected the need for the adult learners to question the importance of the training program and provided satisfactory answers along the way that align with their own agenda? Remember what Oscar said: never assume that these strategies are in place. Assume they are not and embed them to ensure your learners always find their motivation.
Featured in Blog October 30, 2015“Another Brick in the Wall”: Adult Learning versus Pedagogy
 Adult learners have suffered under the spell of pedagogy for many years. It is time for instructional designers to take an active role in making sure executives and those around them understand the fundamental differences between adult learning and pedagogy.
Adult learners have suffered under the spell of pedagogy for many years. It is time for instructional designers to take an active role in making sure executives and those around them understand the fundamental differences between adult learning and pedagogy.
The word “pedagogy” is derived from the Greek words paid, meaning child (the same origin as the word “pediatrician”) and agogus, meaning “leader of”. In essence, pedagogy means the art and science of teaching children. This model of education has been around for a long time (started between the seventh and twelfth centuries evolving from the monastic and cathedral schools in Europe) and it has remained the dominant model of education since. Still today, there are millions of adults being taught like children.
What is the problem with teaching adults like children? There are quite a few, but I want to focus on the most fundamental one in my opinion. In the pedagogical model, the teacher is assigned the full responsibility for the what, the when and the how of the learning that is to take place. It is a teacher-directed education where the learner essentially takes a passive role. And this is where the problem begins. As an adult, we have the need to be self-directed, as Malcolm Knowles emphasized, because being an adult in the first place, according to its psychological definition, is to arrive at the self-concept that we are responsible for our own lives.
In other words, if we break this paradigm and make the clear distinction between adult learning and the pedagogical model, we would start by shifting the responsibility of the learning back to the learner or the adult. We have seen learning and development departments designing eLearning courses, instructor-led training, virtual classroom sessions, and blended learning programs where little to none of the responsibility has been given to the learner. Basic steps to provide the learner with a sense of self-directedness are missing.
An effective instructional designer needs to start by thinking how the learners can take ownership for what is to be learned and how to facilitate* this process. Specific techniques, like allowing learners to pick and choose different delivery methods or engaging in different learning activities that are part of a bigger picture, make a difference and have an impact on the bottom line. Recently, we implemented a simple strategy in this direction at a global manufacturing company which resulted in increased productivity. We assigned ownership to the learners of creating their own support manual relevant to their own needs, thereby reducing their dependency on external support while improving their productivity.
To summarize and extrapolate from Pink Floyd’s Another Brick in the Wall, “Hey! Teachers! Leave them <adults> alone!” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YR5ApYxkU-U
*Facilitator – We can’t force an adult to learn anything but we can facilitate the access to knowledge for those who want it. This concept is behind our name Facilitador, which means facilitator in various languages.
Featured in Blog September 30, 2015Curriculum Design and the Blended Approach
 The purpose of any learning or training program is to help the learner or trainee improve him or herself and the results they achieve for the organization. So if this is this case why not make the learning and training program subservient to how the individual will utilize the learning to improve herself and her organization? And keep in mind that acquisition of knowledge and skills to develop competence and ideally reach a level of mastery does not occur from one day to the next; it is a process that in some cases can take years.
The purpose of any learning or training program is to help the learner or trainee improve him or herself and the results they achieve for the organization. So if this is this case why not make the learning and training program subservient to how the individual will utilize the learning to improve herself and her organization? And keep in mind that acquisition of knowledge and skills to develop competence and ideally reach a level of mastery does not occur from one day to the next; it is a process that in some cases can take years.
We find that when it comes to deciding on a curriculum to prepare individuals for a job role and when leveraging instructional design to deliver this curriculum, most organizations forget the obvious points above.
The first problem is that many organizations try to fit a series of topics, or “things individuals must know” or are “supposed to know” to be successful in their job into an ever expanding curriculum. Chances are that they end up with a huge curriculum that can’t be covered in the amount of time allotted for the training and development program and as a result, critical topics can be left out. The second problem is that many organizations forget the fact that the road to mastery is a process and don’t leverage sound instructional design to support this process.
The first problem is tackled by taking holistic approach to the curriculum and this starts with asking what are successful behaviors of top performers in that role. From there we derive the competencies that need to be developed to execute those behaviors. Then, we ask what are the skills and knowledge that make up those competencies that over time will lead to mastery and lastly, given the aforementioned, how do we make the knowledge and support through this process as least disruptive as possible from the employee’s current work responsibility and environment. Here is where a blended approach is king since it is only through a blended approach that we can find ways for individuals to work and collaborate real time with others, access information when they want it from wherever they want, and access live support on their road to mastery.
Only by taking a holistic instructional approach and leveraging technology can we make the learning subservient to how the learners will utilize the learning to improve themselves and their organizations. We are excited to work with organizations that don’t forget the obvious.
Featured in Blog August 31, 2015
The King of eLearning: Blended
Have you heard the talk when it comes to eLearning that says: “It rarely lives up to its expectations“?
In the mid-90’s and early 2000’s the talk was clear: eLearning would take over the world! Then came the fact that it was self-paced e-learning that was going to give corporations an effective, efficient and economical way of distributing knowledge across the corporation. Then reality struck. Completion rates of self-paced eLearning when not mandatory were below 5% in most organizations and people were complaining left and right when told to take any eLearning course.
It appears that most people forgot that not all eLearning is created equal. There were many electronic page turners (EPT) that were given the name of “eLearning” and since many corporate learning and development departments who purchase and develop eLearning don’t actually consume it (or take it), these EPTs would make it past them. (We jokingly call this “the dog food syndrome” because the owner of the dog – who buys the dog food – doesn’t actually consume it). These EPTs reinforced the perception that eLearning was just not living up to anybody’s expectations evidenced by dismal completion rates and low satisfaction scores.
The bright stars in all of this were the organizations that invested in the right instructional design resources and built real online self-paced interactive learning experiences. This weeded out the organizations that were serious about leveraging the eLearning medium from the ones that didn’t. However, there is a way to ensure that eLearning lives up to its expectations even if we dare call EPTs eLearning, and that is to make eLearning or EPTs part of a blended approach. Obviously, a well developed, instructionally sound course will be able to support a blended approach better than an EPT but both can be designed into a blended approach that doesn’t rely exclusively on the eLearning or the EPT to be effective but on a blended strategy that leverages other mediums like face-to-face instruction, live virtual classrooms, and experiential learning opportunities to achieve tangible results. The concept is that in order for simple eLearning to be king and live up to its expectations, it has to be part of a more robust blended approach.
Featured in Blog July 30, 2015Rocket Fuel for eLearning: Action Plans
Do you want eLearning to have an impact on your people, so your people can have a positive impact on the business?
Yes, that is actually what our research demonstrates. When eLearning is accompanied by an action plan the results go through the roof.
What results? The business results that can be attributed to the training. The reason is simple. An action plan documents how the learner will apply what he or she learned. Accountability is created when the individual completes the action plan and shares it with managers. Hard evidence is created when the individual records the results of his or her application of the action plan. The action plan essentially becomes a link between what is learnt and the impact it had on the business.
An action plan includes any type of document created by a learner that states the actions he or she will undertake in relation to what they have understood to be the learning objectives or goals of any given learning, training, mentoring or coaching program delivered via self-paced e-learning or a virtual classroom. Adult learning theorist Malcolm Knowles describes a series of problems that are solved through the use of action plans, primarily because they allow individuals to develop a sense of ownership and take responsibility for outcomes.
To incorporate action plans into eLearning courses is simple. What is important is that the action plan be structured in a meaningful and relevant way and that it allows for easy access and follow-up. Typically, action plans have been paper-based making them hard to store, retrieve and track. Within an eLearning course they become electronic; the learner can access them when they want; others like managers can view them at any time; learners can complete them at their own pace and make any changes as needed. In a way, the action plan acts a self-regulating mechanism that the individual uses to hold him or herself accountable to apply what they learned. Marshall Goldsmith states in Trigger that our performance improves when we know we will be tested in regards to our personal effort. An action plan commits the individual to exert the effort in applying what they learn with themselves and others.
It’s a simple technique. A powerful one that adds rocket fuel to your eLearning programs. It’s a technique that more often than not gets dismissed and should not. Adding an action plan to an eLearning course can ensure that it positively impacts your people and improves your bottom line.
Featured in Blog June 30, 2015What eLearning content provides the biggest bang for your buck?

Recently, I overheard a conversation at a learning conference when I was waiting to enter a room I was scheduled to present at. The conversation between the two individuals went like this:
“What content provides the biggest bang for your buck? That is the question I have about this e-Learning project we are starting. It’s going to take a lot of effort so knowing what we include and don’t include will be key.”
“Yes we have to look for what’s really going to move the needle so we continue getting funding.”
“I was thinking that what we need to do is make sure we give the people out on the field what they need. They have to tell us what is going to make it or break it for them.”
The question of what is the content that will be most effective within an eLearning solution is very important. Equally or perhaps more importantly is how the knowledge is going to be delivered and how it will be accessed by the learner. Consider the following: in regular face-to-face communications we have three components. They are:
- Our body language
- How we say what we say (voice qualities/characteristics)
- What we actually say or the words we chose
What we actually say represents only about 7% of the equation, with 38% going to how we say it and 55% going to the body language we use when we say it (Mehrabian and Ferris, 1967).
If we were to apply this formula when thinking of an eLearning solution, we would give more weight to how the knowledge will be accessed (55%) than to how the knowledge will be delivered (38%) or what the knowledge is that will be delivered (7%). I am not suggesting that one is more important than the other, but I am suggesting we start by thinking how the knowledge will be accessed by the learner at the point of need.
As adult learners we do not need to remember everything or memorize things, we need to be able to execute our jobs and access knowledge when we need it to support our successful execution of the task(s) at hand. Therefore, any eLearning solution that does not “follow” the learner back when they are on the job will miss the opportunity to provide the most value to that learner at the moment of need.
Now if we consider the content question again under this perspective, we could argue that the ideal content is that which will help our employees perform at their best when they are back on the job. And who knows this best? Our top performing employees. Therefore, the content can come from these employees. How? The best way I have found is through what we call “user-generated content” or self-shot short videos of these top employees sharing specific know-how and best practices to support the successful execution of a task or a step within their jobs. And how will these videos be delivered? It is up to the training department to curate, organize, tag, label, and rank the videos for easy on-the-job access. Creating employee-generated content is not hard if you create the right framework for the training department to be able to accomplish this.
Featured in Blog May 28, 2015Custom eLearning Wars: Will changing your attitude change your behavior or will changing your behavior change your attitude?
Could a generic or off-the-shelf eLearning course change your behavior? Most likely it can’t because it is generic and even though it might have some examples these might not apply to the specific situations your employees will face. Could a generic eLearning course change your attitude or how you think about something? Perhaps it can if the content is valid and the generic e-Learning course has been well designed. However, does changing your thinking about something guarantee that you will change your behavior? The answer quite simply is no, nothing can guarantee it (think about how many times you read a life changing health practice and then failed to apply it) but you can put the odds in your favor.
Now let’s consider the following: can changing behavior change the way we think about something? The answer is yes. Ultimately it is behavior that counts since it is what impacts the world around us. How can behavior change our thinking? Let’s consider some examples where this might seem obvious. The first is dressing differently (a behavior). When we are dressed in fancy, expensive clothes or in a uniform, we tend to change how we stand, how we talk, and how we perceive ourselves. Another example is when we force ourselves to smile (a behavior). In the beginning, it might feel awkward and fake, but as we maintain the smile we start feeling happy (thinking happy thoughts). If you are still not convinced, try the smile technique on your own (perhaps do so in private so people around you don’t think you are crazy!)
So how do you increase the odds of a behavior change occurring after an eLearning course? You not only provide relevant, valid and compelling content to impact how people think about an issue or as Peter Senge of Harvard would describe, change the mental models people hold to interpret what is around them, but you also provide examples that are specific to the challenges and situations your employees will face. Modeling the right behavior within the appropriate context can be achieved only through a custom eLearning course that has been designed based on your employees’ specific needs and challenges. When the behaviors are made explicit in this manner, the gap between knowing something and being able to execute on it, or what Jeffrey Pfeffer and Robert I. Sutton coined “The Knowing-Doing Gap,” is shortened. It is still not a guarantee people will change their behavior as this responsibility ultimate lies with the individual, but the odds will definitely be in your favor.
Featured in Blog April 20, 2015
5 Best Practices to Help you Create Content for Custom eLearning
We constantly hear it from our clients. And now Brandon Hall has validated our experience. According to Brandon Hall Group’s 2014 Business Focus Survey, content development is one of the biggest concerns for a learning organization, and sourcing that content is often a challenge. 62% of companies surveyed stated that content development is either a high priority or critical to their business. Sourcing this content for custom eLearning courses is sometimes a challenge since most of what is available out there is generic, off-the-shelf material that is usually not relevant.
So what do they do?
They hire us. (Ha ha ha! Had to get that one in there…)
What happens is most times, companies try to build their own content. And this can be tricky if a process and certain critical steps are not taken into account. Here are our 5 best practices for helping our clients compile and create great and effective content for elearning courses:
1) Project Management: Make sure you have a project manager who will own the content creation task and keep people on track. It’s a good idea to have an executive sponsor to hold people accountable to deadlines.
2) Content Outline: Determine a content outline that will meet your overall training objective. Usually the best way is to meet with the SME’s and stakeholders and zero in on the most important parts needed to ensure learning objectives will be met.
3) Gather Existing Content: Gather any existing relevant content and identify any gaps. Fill in the gaps by developing any new content needed. Interviewing SMEs and top performers is your best bet for new content. When confronted by an unresponsive internal SME, get the executive sponsor involved!
4) Analyze and Synthesize: Categorize the content into need to know versus nice to know content and have the SMEs and sponsors sign off on it.
5) Instructional Design is King: Have expert instructional designers who will know how to take this content and turn it into an engaging and effective learning experience that focuses on how learners will apply the knowledge learned when they are back on the job.
Featured in Blog March 19, 2015Custom eLearning Wars: Great Learning Experience vs. Application of the Training

How often do we design learning experiences thinking about how the learners will use the knowledge when they are back on the job?
Many custom eLearning companies will emphasize the need to create great learning experiences. Elearning consultants may emphasize that multimedia, animations and other wow factors will lead individuals to have a meaningful experience. However, in a corporate training and development department or workplace learning setting, the objective is to impact performance in a way that advances the organization’s objectives. Therefore, should we as instructional designers concern ourselves more with creating a great learning experience or do we focus more on enabling the performance that needs to happen after the learning experience? In our experience working with leading organizations that range from multinationals to progressive startups, we have seen that ensuring the success of the learners when the time comes to act is the most important function of the custom eLearning or custom training and development solution. The fact that the learning experience was great will be meaningless if it does not equip the learner to succeed when they are back on the job.
Anticipating how learners will use the knowledge when they are confronted with the realities and pressures of the job, can guide the instructional designer to incorporate specific strategies to leverage this context and to incorporate informational, procedural or decision-making job-aids at the point of need. The instructional designer’s input can and should go beyond the learning experience.
Featured in Blog February 26, 2015Meaningful and relevant eLearning? Customize it!
Arguably, anyone can benefit by taking ownership of how and what to apply from a custom online training program. Arguably, anyone can benefit from being encouraged to do so and very importantly, anyone can benefit from receiving feedback on the actions they take so they can improve the application or use of the knowledge acquired from a custom online training program.
As obvious as this sounds, the lack of follow-through on applying what is learned and specially in online training programs plagues millions of employees here in the U.S. and worldwide. As such, it is estimated that 90 percent of job-related skills and knowledge imparted in online training programs are not being implemented.
The numbers could be even worse if we consider only e-learning and not instructor-led training. Many consultants, like training consultants, business consultants and even e-learning consultants would agree. From the individual’s perspective, there is also a huge cost since they might not take advantage of the elearning or online training opportunity to enhance their performance or contribution to the company’s goals and could lose potential career advancements as a result.
The solution to this problem is to ensure that your online training is customized to your needs. Sounds simple, yet many organizations fail to recognize that e-learning which is not customized will not be meaningful and relevant to their employees. Online training that is not custom e-learning may provide good and valid concepts that may have been designed with the best intentions but it leaves a huge gap for the employees to fill. The gap is created by leaving it up to the employee to take those concepts and translate them into specific situations or challenges they encounter on the job. Unfortunately, not all of us have the will or skills to fill in this gap successfully, especially since generic e-learning can be quite vague trying a one-size fits all strategy.
In summary, custom online training or custom e-learning considers all the potential factors that can impact success and allows you to create a program that delivers true business value. Not all e-learning is the same and certainly not when it’s customized to your needs. Custom e-learning programs can have a direct impact on your company’s bottom line and this can be demonstrated.
New Year, New Face
We have many reasons to celebrate.
First, we begin this new year with a new face which we believe more closely represents the type of work that we have been privileged to do for the past 14 years. Our new logo showcases how we have been breaking barriers, thinking outside the box and creating innovative and transformational training and development solutions that have impacted the lives of millions of people by leveraging the latest elearning and virtual classroom technologies. Our commitment to making sure the knowledge our training programs impart is transformed into action is now clearly portrayed both in the logo and the site itself. (More on this topic later).
Second, we have decided to make available and share with you the knowledge and best practices we have acquired over these years through our new Thoughts in Action section. We will be highlighting specific and common issues that can get in the way of completing training programs and how to stay focused on designing and implementing a program that takes into account how individuals will use the knowledge provided. In fact, research has shown that up to 90% of the knowledge taught does not get applied. We realize that the only way our clients will reap the benefits of any training program is if it turns into action.
So we are constantly asking ourselves: what strategies can we include to allow learners to extract the knowledge they need when they are back on the job from this learning experience? Job aids, action plans, reference guides, quicktutorials, etc. are some of the strategies our team uses to make sure the knowledge is easily accessible after the training at the time of need.
We hope you like our new site and our focus on transforming knowledge into action. We welcome your feedback to make it even better!
Featured in Blog